1. Define the unit cell and write its size and atomic position.
Inside a solid, countless atoms are arranged in regular. The minimum repeating pattern is defined as a unit cell. To use computer resources efficiently, it is recommended to use the primitive unit cell.
Graphene’s primitive unit cell is described by a rhombus. You can save the file below to draw the atomic structure of graphene.
graphene a = 2.700000
2.46380000000000
1.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000
-0.50000000 0.86602000 0.00000000
0.00000000 0.00000000 20.000000
C
2
Direct
0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000
0.33333333 0.66666666 0.00000000
2. Save the information as a plain text (*.vasp).
MacOS/Linux
2.1 Open the Terminal. (& Go to the directory you want to save in Finder.)

2.2 Create a file.
Enter the command below into the terminal to create a geometry file in Desktop path.
cd Desktop
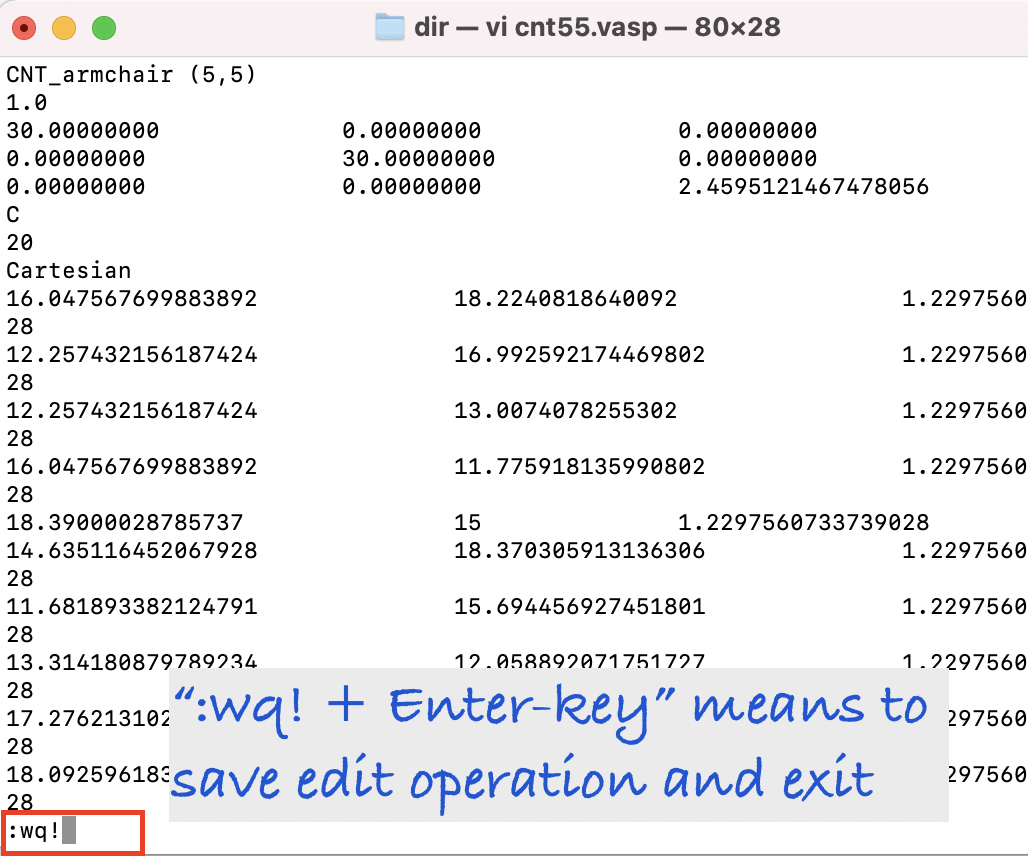
vi cnt55.vasp
-
- cd Desktop
- Command to enter your Desktop directory
-
- vi cnt55.vasp
- Command that opens a file named cnt55.vasp. If the file does not exist, it creates the cnt55.vasp plain text file with empty text.
How to write a file:
(1) The first thing you need to do is to press the “I key” on your keyboard. This allows you to enter the insert mode.

(2) Next, you should paste the geometry data(copy & paste).

(3)You can escape from the insert mode by pressing the Esc key.

(4) You then type :wq! + enter-key and can save the changes.
Windows
2.1 Open Notepad and paste the text.
2.2 Save the file as *.vasp.
3. Open VESTA and drag and drop the file.
VESTA is a tool that models files representing atoms and molecules such as *.vasp, *.cif, *.xyz, etc.